Choosing the right measurement geometry
Important: The choice of the measurement geometry depends on the application!
Before you buy a spectrophotometer, the correct measurement geometry must be selected.
The quality of the color control methods and the reproducibility of the measurement values does not depend on the particular advantages or disadvantages of the measurement geometry.
The most important criterion when choosing the measurement geometry is the sample application. In addition, there are international standards and norms for many industrial areas that specify the measurement geometry. In order to be able to compare measured values from different spectrophotometers, a matching measuring geometry is required. That means customers, suppliers and individual locations should use the same measurement geometry.
We would be happy to advise you and give support to have best instrument agreement.
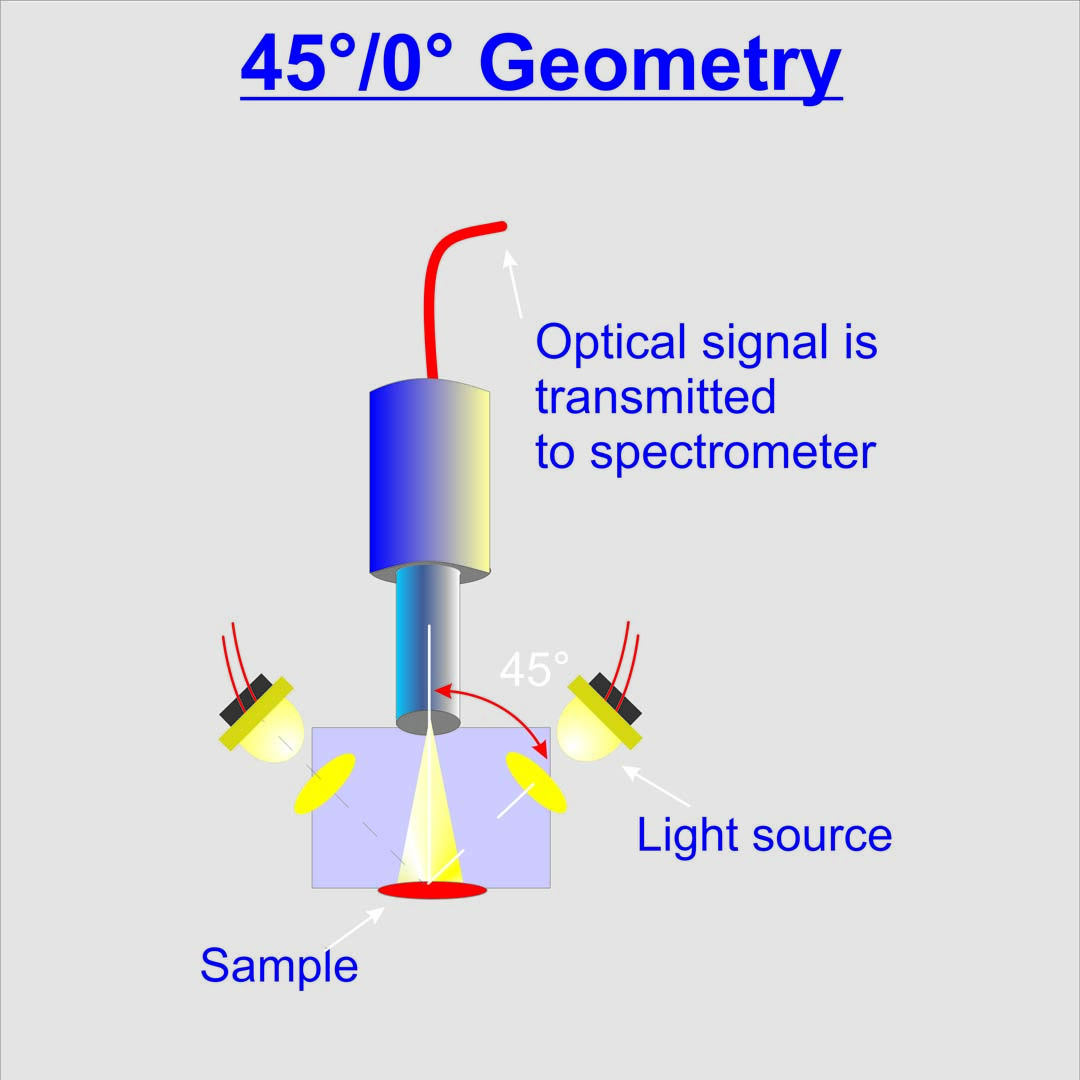
45°/0° Closest to the eye
The 45/0° measurement geometry describes the in DIN Norm 5033 standardized measurement geometry. The probe is illuminated by an difuse light source in a 45/° angle and the than reflected light is being measured.
Note: For measuring effect varnishes mulit angle spectrophotometers are needed.
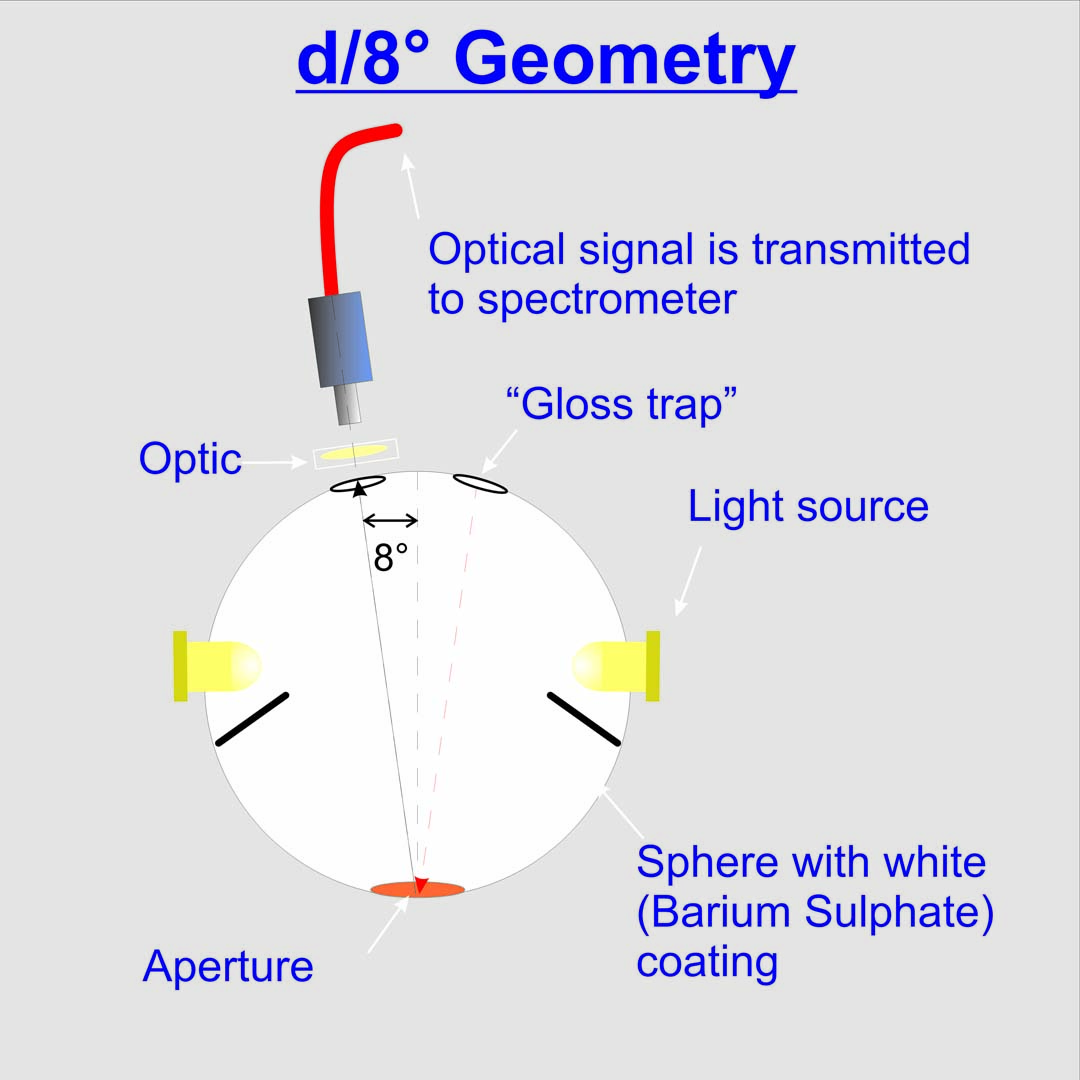
d/8° Integrated sphere geometry
The d/8° measurement geometry is described in DIN Norm 5033. The probes are illuminated thru a diffuse light source with an 8° angle. The diffuse light is being generated by an integrated Ulbricht sphere. The gloss reflected from the surface is being measured with diffuse light.
Measurement with specular excluded (SCE) or specular included (SCI)
When measuring with a sphere geometry it is differentiate after two measuring geometry’s:
SCE (Specular Component Excluded)
The gloss trap is being opened so the glossy component can leave the sphere. The colour is beeing measured without gloss.
SCI (Specular Component Included)
The gloss trap is staying closed. The entire reflecting light meaning colour and gloss are measured.
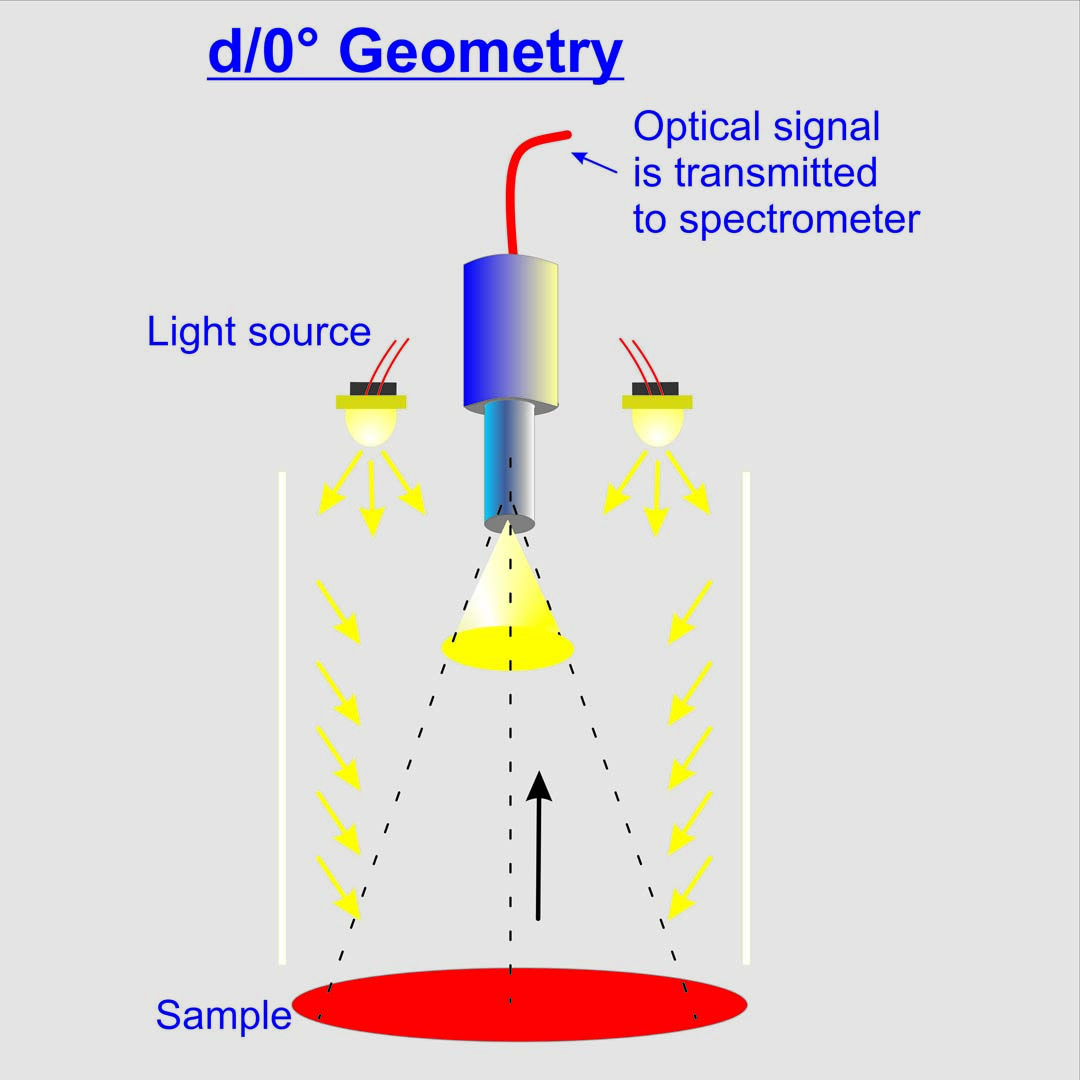
d/0° Making inhomogeneous samples measureable
The d/0° measuring geometry is illuminating the probe diffuse. The measurement geometry is used to measure inhomogeneous probes such as granules, food or wood paint. This measuring geometry is not normed.